Incentive Stock Options (ISOs) are a common type of employee stock benefit that provides certain tax benefits. Companies frequently use them to draw in and keep skilled workers. But, it's crucial to comprehend how ISOs operate, their possible gains, as well as the risks linked with them before deciding whether or not to accept or exercise these options. This article will walk you through the details of ISOs, concentrating on their main characteristics, their image pact on taxes, and what workers need to think about before exercising these stock options.
What Are Incentive Stock Options (ISOs)?
Incentive Stock Options represent a form of employee stock option that offers more advantageous tax handling compared to other types of stock options, like non-qualified stock options. These permit employees the opportunity to buy a certain number of shares in the company they are employed by at an already decided price, frequently called an exercise or strike price. This price is generally less than the market value when these options are given out. ISOs are created to motivate employees to remain in the company and aid its expansion because these options frequently have vesting periods and performance needs.
ISOs, different from other stock options, are controlled by certain laws under the U.S. Internal Revenue Code. These rules provide ISOs with unique tax benefits c they enjoy. But this equally means that more strict standards come along with ISOs like restrictions on the quantity of stock allowed to be granted and the waiting time for shares after execution. When it is rightly formatted, ISOs can provide a way for employees to reap benefits from their company's growth and at the same time reduce their tax responsibilities.
The Key Benefits of Incentive Stock Options
A significant advantage of ISOs is the possibility of beneficial tax handling. If employees use and sell under suitable conditions, they have a chance to not pay regular income tax on the gap between them.gn exercise price and the market price at the purchase moment. Rather, their earnings could be subject to taxation at less long-term capital gains rate if specific criteria are satisfied. For a lot of workers, this could lead to substantial tax reductions when compared to other types of equity payment.
Besides the benefit of tax, ISOs give workers a chance to buy company shares at a reduced price. This can bring about great monetary profit if the firm's stock value increases over time. By permitting employees to purchase business stocks at a set cost, even when their worth goes up dramatically, ISOs may be an outstanding method for becoming part of their employer's financial progress.
ISO Tax Implications - What You Need to Know
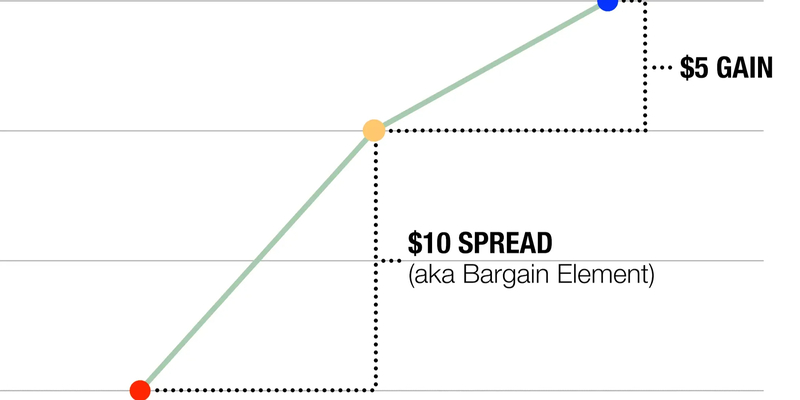
Knowing how ISOs can impact your taxes is important if you are thinking about including them in your pay package. When you use an ISO, there's no need to give tax on the gap between its exercise price and market value when you exercise it, provided certain holding terms are met. To get this good tax treatment, keeping hold of these shares for not less than one year after their date of exercise plus two years following the granting of the option is necessary.
When you sell the shares without waiting for this holding period, it is seen as a disqualifying disposition. This means profit from such sales will be taxed like regular income and not at a long-term capital gains rate. This situation can result in more tax liability. Also, there may be additional effects, if when exercising an option, the difference between exercise price and market price exists, it might activate alternative minimum tax (AMT). AMT is a different kind of tax calculation that could enhance the overall amount of your taxes within a year where options are exercised by you.
You should coordinate with a tax advisor to grasp the complete tax effects of ISOs and how they blend into your overall financial situation. This will assist you in deciding the top strategy for using your options and might lessen your tax load potentially.
The Risks of Incentive Stock Options
Although ISOs provide substantial advantages, they also carry risks. A major risk relates to the performance of the company's shares. If the value of a firm's stock falls, these options can become worthless and employees might obtain meager or no financial gains from their investment options. It is particularly worrying if workers put a big part of their own money into the company's shares, or they use their choices too soon.
Another danger linked with ISOs is possible tax responsibility. Although the tax handling of ISOs may be beneficial, the AMT might cause unforeseen tax outcomes, particularly for persons who possess a big difference between the exercise price and stock market price. If you utilize a considerable number of options and if there's a quick increase in stock value, then AMT could lead to an unanticipated taxation invoice.
If the business's share price remains fairly steady or does not increase as anticipated, workers may discover that their ISOs do not offer as much economic advantage as they initially envisaged. Consequently, it is crucial to meticulously assess the financial condition of the company, stock performance, and expansion potential before deciding on exercising ISOs.
How to Exercise Incentive Stock Options
When you exercise ISOs, it means that you buy the company's shares at a set price and then own these shares. Workers usually have only a short time duration to use their options after they get them vested. Hence, they need to make up their minds about whether they should move with their options or let them expire. It is very important not to forget that exercising ISOs might necessitate a big amount of cash payment, especially if share prices are higher than when the options were given initially.
Before you exercise your options, reflect upon your financial situation, the present value of the stock, and your future investment objectives. In certain situations, it can be wise to wait for more appreciation in stock or delay exercising the options until nearing the end of the vesting period. Evaluating tax effects when using these options is also crucial so discussing with a tax advisor could help make a knowledgeable choice.
Conclusion
The offering of Incentive Stock Options is quite a charming method for employees to reap rewards from the triumphs of their company while also possibly gaining tax benefits. But, the choice to take and utilize ISOs mustn't be taken in an easy-going manner. Workers need to think through with caution about tax consequences, potential hazards, and the complete fiscal well-being of their firm before proceeding with these options offered. Talking to a financial or tax expert can assist you in making decisions that match your monetary objectives. By knowing the specifics of ISOs and what they mean, workers can fully utilize this staff stock bonus for sustainable economic development.







