Respiratory therapy is an important part of healthcare. This type of therapy focuses on helping people who can't breath the right way. Breathing problems can come from illnesses, injuries, or even age, and they can greatly affect a persons quality of life. This is where respiratory therapists come inthey are trained to help people breathe better by using special tools, treatments, and care plans. They work with patients of all ages, from newborns to the elderly, providing both short-term relief and long-term support. In this article, well explore the role of respiratory therapists, what they do, and why they are so valuable in healthcare.
What Is a Respiratory Therapist?
Respiratory therapist is a type of therapist who specializes in treating patients with breathing or lung-related problems. They work closely with doctors and nurses to develop and carry out treatment plans that help patients breathe easier and manage their respiratory conditions. Respiratory therapists get a wide range of patients in their office. They deal with premature babies who have underdeveloped lungs, adults experiencing chronic lung diseases like asthma, COPD, and pneumonia. They monitor their patients oxygen levels, provide breathing treatments, and manage ventilators for their clients. They provide essential care for the patients and guide them through their symptoms.
What Does a Respiratory Therapist Do?
A respiratory therapists job is to help people who have problems with breathing. Each day, they do many tasks to support patients, including tests to check lung health, planning treatments, and teaching their clients how to care for their lungs. Respiratory therapists also perform specific procedures, like giving oxygen therapy to help patients breathe better, setting up and managing ventilators, and acting quickly in emergencies to assist with breathing. They work with people of all ages, in many places, from hospitals to home care. This mix of tasks makes respiratory therapists an important part of helping people live and breathe better.
Common Conditions Treated by Respiratory Therapists
Respiratory therapists (RTs) help treat many common lung and breathing conditions. Each condition has unique needs, and RTs use their skills to make breathing easier for people of all ages. Below are some key conditions and how RTs support patients with each one.
Asthma
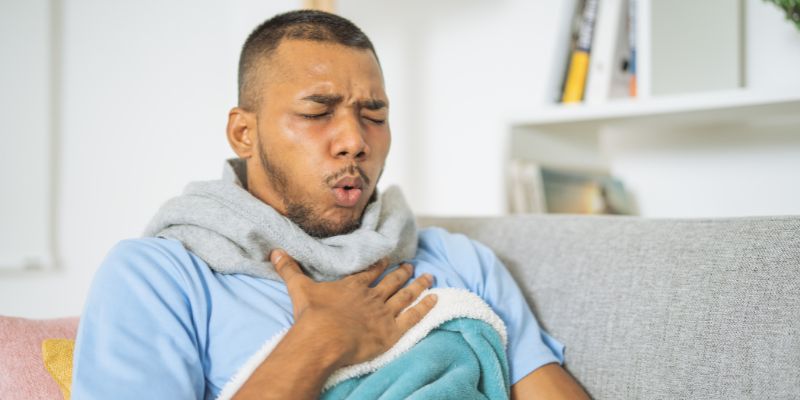

Asthma causes the airways to tighten, making it hard for people to breathe. During an asthma attack, someone may feel short of breath, cough, or wheeze. RTs help asthma patients by teaching them how to use inhalers and other breathing devices, showing them ways to manage attacks, and providing breathing exercises to keep airways open. In emergencies, RTs may give oxygen or other treatments to help the patient breathe more easily.
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
COPD includes various other diseases (like chronic bronchitis and emphysema) where the lungs are damaged and breathing becomes harder over time. Patients with COPD often feel tired and short of breath. RTs support these patients by setting up oxygen therapy, helping them with breathing exercises, and teaching them ways to save energy during daily tasks. They may also assist with medications that open airways, which makes breathing easier.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a type of infection that happens in lungs (mainly due to fluid build up) that can make it hard to breathe and cause coughing and chest pain. RTs help patients with pneumonia by providing oxygen therapy if needed, showing them how to clear mucus from their lungs, and helping them do deep breathing exercises to improve lung function. This helps speed up recovery and make breathing easier.
Sleep Apnea
In sleep apnea, a persons breathing stops and starts while they sleep. This can hinder their sleep quality and lead to other health issues. RTs help sleep apnea patients by fitting them with devices like CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) machines, which keep the airways open during sleep. They also teach patients how to use these machines at home for better rest and health.
Role of Respiratory Therapists
Respiratory therapists help manage these and other conditions by providing care that makes breathing easier, improves lung health, and helps patients live more comfortably. Through treatments, training, and support, RTs help patients take control of their breathing and feel their best.
Education and Training Required to Become a Respiratory Therapist

Becoming a respiratory therapist (RT) requires a mix of schooling, hands-on experience, and certification. Here is a step-by-step look at the path to becoming an RT.
1. Get a High School Diploma
A high school diploma is the first step. Classes in biology, chemistry, and health are helpful for building a strong foundation in science.
2. Complete an Associates Degree (2 Years)
Most respiratory therapists need at least an associates degree from an accredited program. These programs include courses in anatomy, physiology, and respiratory care. These students also perform practical acts in the labs to learn more about how these breathing devices work and how to provide oxygen therapy.
3. Gain Clinical Experience (Part of Degree Program)
During their studies, students must complete clinical training, working directly with patients under supervision. This hands-on practice allows them to learn how to assist with breathing treatments and use medical tools.
4. Pass the National Certification Exam
After finishing school, students must pass a national test called the Certified Respiratory Therapist (CRT) exam. Some go further and take the Registered Respiratory Therapist (RRT) test for advanced certification.
5. Consider Specializations
Respiratory therapists (RTs) can choose to specialize in other areas like adult critical care or neonatal care, working with newborns, etc. Additional training or certifications may be required for these areas.
Overall, the total time required to become a respiratory therapist can be around 4 years. Through each of these steps, respiratory therapists (RTs) learn the skills and gain the experience they need to provide safe, effective care for patients with breathing challenges.
Conclusion
From treating conditions like asthma, COPD, and sleep apnea, to using special skills and tools, respiratory therapists (RTs) work hard to improve patients lives. We also covered the steps needed to become an RT, including school, hands-on training, and certification. With their knowledge and care, respiratory therapists make a real difference for people of all ages. They help patients breathe easier, live healthier, and feel better, showing just how valuable their work is in healthcare every day.